The level of investment into research and development has grown tremendously, with global spending expected to reach $2.476 trillion in 2022 alone. A robust intellectual property strategy is critical to protecting return on investment for new innovations. Understanding relevant patenting activity and conducting a prior art analysis before investing in an area is essential. Suppose disclosures have been made before your innovation’s patent filing date. In that case, the patent application will be rejected, so it is critical to identify relevant prior art early in the R&D process to determine future patentability.
Doing so can allow organizations to develop strategies to differentiate the innovation during the development and patent drafting stages and avoid wasted R&D spending.
Incomplete searches can lead to costly mistakes in IP strategy, given the significant amount of money invested in pre-market research and development of new inventions. Consequences of incomplete prior art analysis include rejection of patent applications, patent infringement, or invalidation of existing patents. For these reasons, understanding how to conduct an effective and thorough prior art analysis is crucial.
Where are prior art references found?
The most common place to begin a prior art search is with existing patents and patent applications. Rejected, pending, and abandoned patent applications can also be considered prior art if they disclose your innovation — wholly or in part. In addition to patent documentation, you can find prior art in non-patent literature, such as peer-reviewed publications, dissertations, conference presentations, and other similar disclosures.
The digitization of materials such as books, illustrations, objects, analog recordings, and photos has increased the volume of searchable materials to find prior art. At the same time, the volume of scientific publications is growing exponentially, leading to an increase in the amount of information required to review for a thorough prior art analysis. Moreover, modern-day scientific innovation often happens at the intersection of many disciplines. For these reasons, comprehensive prior art analysis is time-consuming and complex to navigate.
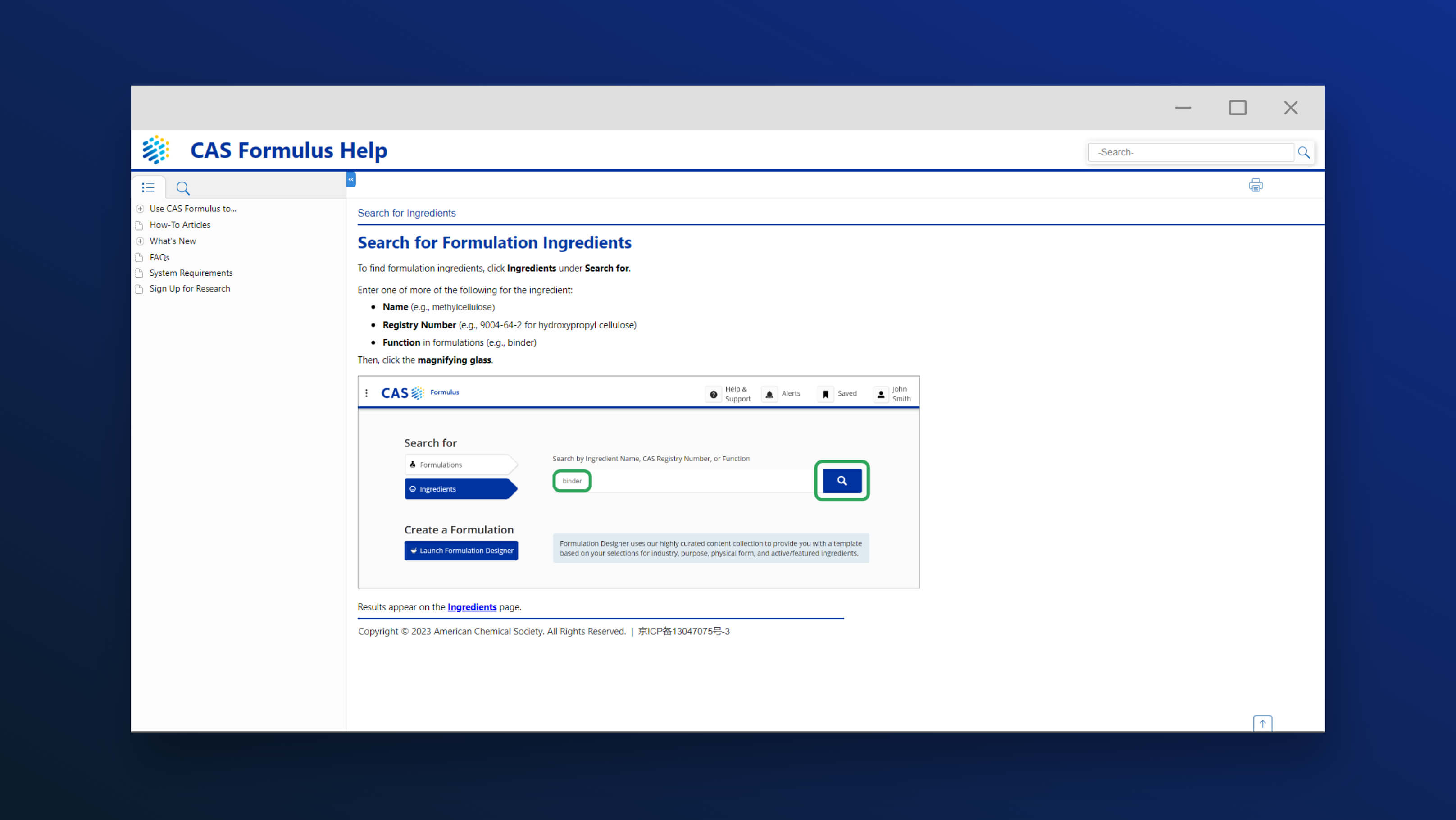
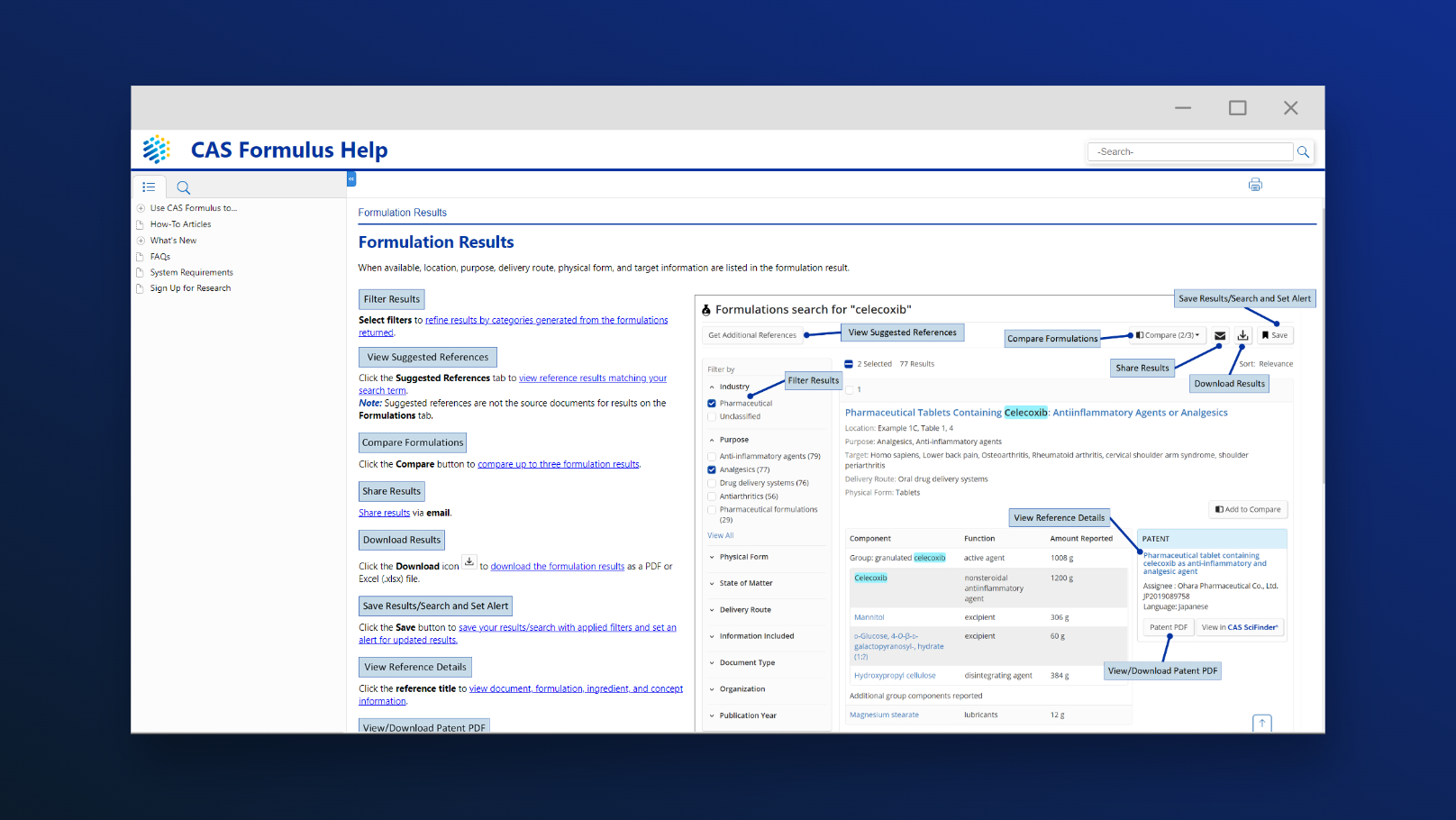
CAS STNext® enables comprehensive prior art analysis by providing searchers with integrated access to the most current and complete collection of globally disclosed patent and non-patent, scientific, and technical content.
CAS combines over 100 diverse data collections, including leading chemistry content from the CAS Content CollectionTM — a comprehensive collection of databases and curated sources containing patent and non-patent literature. It is one of the few sources for searchable global patent Markush disclosures, containing over 1.2 million searchable Markush structures covered in patents from 1988 to the present, and is updated daily.
IP professionals can access these rich and authoritative datasets through CAS STNext, which offers an advanced interface and powerful precision search capabilities. By adding CAS STNext to your toolkit, you can thoroughly assess risks and commonalities with the prior art and guide smarter, data-driven decisions.
Explore the capabilities of CAS STNext.
How to identify appropriate search sources for prior art analysis
IP searchers have various options for sources when planning a prior art search strategy, and choosing the right resources is critical. If you're looking for a broad overview of the patent landscape, search engines and patent office interfaces are helpful places to start. However, these sources could be more extensive in their functionality and coverage. Many open-source search tools need more customized algorithms to navigate complex scientific information, such as chemical formulas and biological processes. Another major hurdle of open-source search engines is that, in many cases, they cannot pull information from documents such as image-based PDFs. Additionally, many open-source search engines don’t include the breadth of information needed to capture relevant documents. This causes gaps in prior art searches.
To close these gaps, IP analysts rely on multiple sources. Those innovating in scientific industries turn to trusted search platforms like CAS STNext to support an efficient and comprehensive review of existing literature and scientific information. In addition to enabling search across multiple sources, CAS STNext leverages cutting-edge technology and expert human curation to support precision searching and identify documents that are generally difficult to find—even for experienced IP researchers. CAS STNext also offers an “index look up” feature and artificial intelligence to enable searchers to identify the relevant information for their technology of interest quickly.
Check out this webinar to learn how CAS STNext uses artificial intelligence to boost your prior art analysis.
Defining the scope of a prior art search
When formulating a prior art search, it is critical to consider the currency and coverage of your sources. Searchers must consider the legal requirements of the search and understand the details of what information is covered (or not covered) within individual sources.
It is crucial to understand the details of the publication dates, content update schedule, country coverage, etc., of your sources to ensure your search meets the legal requirements of the requesting stakeholder.
Review the search scope periodically to ensure that it remains relevant and up-to-date. If the product strategy changes (for example, to expand into new global markets), it is vital to understand the scope of the original search to determine if the conclusions hold for the new requirements. This can help identify any potential gaps in the search and ensure that the conclusions drawn are reliable.
Check out this article, which explains the importance of casting a wider net in a prior art search.
How to formulate an appropriate prior art query
When it comes to formulating the best prior art query, clearly defining the technical features of the invention is essential. A clear understanding of the technical features allows you to determine the relevant search terms (including synonyms) and sources for the search, reducing the chances of missing any relevant prior art.
Some considerations when identifying appropriate keywords include spelling variations, keywords in foreign languages, and historical terms for different patent classifications.
The field of innovation shapes the query. For example, querying a chemical structure for chemistry-based inventions can be an effective strategy for conducting an effective prior art analysis. In contrast, a query for numerical information such as pH ranges or temperature is an effective method in engineering. A precise query will save time during the post-search review and help identify prior art that less sophisticated methods may miss.
How do you know when you have completed a thorough prior art analysis?
Deciding when it’s a good idea to stop searching is an important and challenging decision. One of the best ways to determine when to stop is by the principle of convergence. This can be accomplished by searching in different ways, such as using many keywords, citations, competitor reviews, or chemical information, and checking if the query returns the same results. Once the results converge, it’s safe to say that the search is thorough.
Applying this principle is essential for maximizing the value of your search strategy. Searching without convergence could mean missing important keywords or search terms, leading to a prior art analysis that misses crucial pieces of the prior art. At the same time, searching too deeply can be time-consuming and expensive without generating additional meaningful results.
Look at this article, which explains key points to consider when conducting a prior art search.
Consulting professionals with expertise in your industry and in prior art analysis will save you time and money
Comprehensive prior art searches are often conducted late and are incomplete, leaving the organization and its R&D pipeline at risk. The cost of missing relevant prior art is high; in 2020, the United States courts awarded $4.67 billion in damages for patent infringement. It is imperative to identify prior art before investing in R&D and to continue identifying new prior art after the innovation is successfully developed.
Even with top-tier IP search tools, ensuring your prior art analysis is airtight is challenging. Working with technology and IP search experts to assist in conducting comprehensive prior art searches can save time while ensuring that no piece of prior art is missed.
Consider CAS
The CAS team comprises knowledgeable experts in chemistry and the life sciences, as well as in prior art analysis. Hundreds of scientists work daily to build the CAS Content Collection, ensuring that complex aspects of patent documents, including chemical substances, sequences, and Markush structures, are searchable and easily accessible.
This unique wealth of knowledge underpins CAS’s abilities, enabling them to curate comprehensive databases, offer reliable IP tools such as CAS STNext for self-service searches, and provide trusted search support when needed.
Get in touch to learn more about CAS STNext or to organize a demonstration of CAS IP solutions in action.
Gain new perspectives for faster progress directly to your inbox.